25 Essential Excel Formulas List 2025
Are you still using basic Excel functions like SUM and IF? It’s time to upgrade your Excel skills with 25 Essential Excel Formulas List 2025 that can transform how you analyze and manage data in 2025 — including both classic functions and powerful Excel 365 additions.
Table of Contents
🧠 Why You Must Master Excel Formulas
Whether you’re a data analyst, accountant, manager, or student — knowing the right Excel formula at the right time can save hours and reduce errors. These formulas can help you:
- Automate calculations
- Extract insights from data
- Create dashboards
- Clean and organize information
- Improve productivity
Now, let’s dive into the 25 Essential Excel Formulas List 2025 you should master this year.
📌 Why Learn These 25 Essential Excel Formulas List 2025?
- Save 10+ hours weekly by automating repetitive tasks
- Make fewer errors than manual calculations
- Get promoted faster by demonstrating advanced Excel skills
- Work more efficiently across finance, marketing, HR, and operations
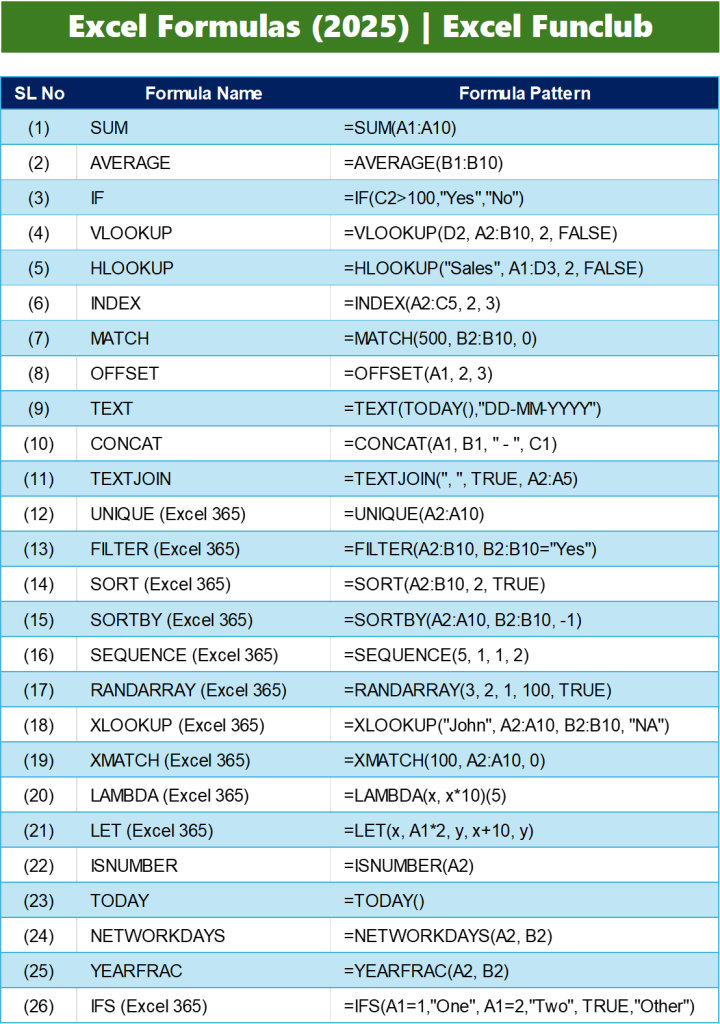
📊 25 Essential Excel Formulas List 2025 (With Examples)
Here’s the full list of Excel formulas, categorized by their function, along with syntax patterns for quick reference:
| SL | Formula Name | Formula Pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SUM | =SUM(A1:A10) |
| 2 | AVERAGE | =AVERAGE(B1:B10) |
| 3 | IF | =IF(C2>100,"Yes","No") |
| 4 | VLOOKUP | =VLOOKUP(D2, A2:B10, 2, FALSE) |
| 5 | HLOOKUP | =HLOOKUP("Sales", A1:D3, 2, FALSE) |
| 6 | INDEX | =INDEX(A2:C5, 2, 3) |
| 7 | MATCH | =MATCH(500, B2:B10, 0) |
| 8 | OFFSET | =OFFSET(A1, 2, 3) |
| 9 | TEXT | =TEXT(TODAY(),"DD-MM-YYYY") |
| 10 | CONCAT | =CONCAT(A1, B1, " - ", C1) |
| 11 | TEXTJOIN | =TEXTJOIN(", ", TRUE, A2:A5) |
| 12 | UNIQUE (Excel 365) | =UNIQUE(A2:A10) |
| 13 | FILTER (Excel 365) | =FILTER(A2:B10, B2:B10="Yes") |
| 14 | SORT (Excel 365) | =SORT(A2:B10, 2, TRUE) |
| 15 | SORTBY (Excel 365) | =SORTBY(A2:A10, B2:B10, -1) |
| 16 | SEQUENCE (Excel 365) | =SEQUENCE(5, 1, 1, 2) |
| 17 | RANDARRAY (Excel 365) | =RANDARRAY(3, 2, 1, 100, TRUE) |
| 18 | XLOOKUP (Excel 365) | =XLOOKUP("John", A2:A10, B2:B10, "Not Found") |
| 19 | XMATCH (Excel 365) | =XMATCH(100, A2:A10, 0) |
| 20 | LAMBDA (Excel 365) | =LAMBDA(x, x*10)(5) |
| 21 | LET (Excel 365) | =LET(x, A1*2, y, x+10, y) |
| 22 | ISNUMBER | =ISNUMBER(A2) |
| 23 | TODAY | =TODAY() |
| 24 | NETWORKDAYS | =NETWORKDAYS(A2, B2) |
| 25 | YEARFRAC | =YEARFRAC(A2, B2) |
| 26 | IFS (Excel 365) | =IFS(A1=1,"One", A1=2,"Two", TRUE,"Other") |
1. SUM
Formula: =SUM(A1:A10)
Use Case: Adds up all numbers in a specified range.
Example:
=SUM(A1:A10)→ Sums values from A1 to A10.
Why It’s Useful:- Quickly calculate totals for budgets, sales, or inventory.
2. AVERAGE
Formula: =AVERAGE(B1:B10)
Use Case: Calculates the mean of numbers in a range.
Example:
=AVERAGE(B1:B10)→ Finds the average of B1 to B10.
Why It’s Useful:- Helps analyze performance metrics, grades, or survey results.
3. IF
Formula: =IF(C2>100,"Yes","No")
Use Case: Performs conditional checks.
Example:
=IF(C2>100,"Above Target","Below Target")→ Returns “Above Target” if C2 > 100.
Why It’s Useful:- Automates decision-making in reports (e.g., pass/fail, bonus eligibility).
4. VLOOKUP
Formula: =VLOOKUP(D2, A2:B10, 2, FALSE)
Use Case: Searches for a value in the first column of a table and returns a corresponding value.
Example:
=VLOOKUP("Product1", A2:B10, 2, FALSE)→ Finds “Product1” and returns its price.
Why It’s Useful:- Great for retrieving data from large datasets (e.g., employee records, product prices).
5. HLOOKUP
Formula: =HLOOKUP("Sales", A1:D3, 2, FALSE)
Use Case: Searches for a value in the first row and returns a value from a specified row.
Example:
=HLOOKUP("Sales", A1:D3, 2, FALSE)→ Finds “Sales” in the first row and returns the value from row 2.
Why It’s Useful:- Useful for horizontal data lookups (e.g., quarterly sales reports).
6. INDEX
Formula: =INDEX(A2:C5, 2, 3)
Use Case: Returns a value from a specific row and column in a range.
Example:
=INDEX(A2:C5, 2, 3)→ Returns the value in the 2nd row and 3rd column of A2:C5.
Why It’s Useful:- Helps extract precise data points from large tables.
25 Essential Excel Formulas
7. MATCH
Formula: =MATCH(500, B2:B10, 0)
Use Case: Finds the position of a value in a range.
Example:
=MATCH(500, B2:B10, 0)→ Returns the row number where 500 appears in B2:B10.
Why It’s Useful:- Often combined with INDEX for advanced lookups.
8. OFFSET
Formula: =OFFSET(A1, 2, 3)
Use Case: Returns a reference offset from a starting cell.
Example:
=OFFSET(A1, 2, 3)→ Returns the value 2 rows down and 3 columns right from A1.
Why It’s Useful:- Dynamic range selection for dashboards and charts.
9. TEXT
Formula: =TEXT(TODAY(),"DD-MM-YYYY")
Use Case: Formats numbers or dates as text.
Example:
=TEXT(TODAY(),"MMMM DD, YYYY")→ Displays “June 14, 2025”.
Why It’s Useful:- Ensures consistent date/number formatting in reports.
10. CONCAT
Formula: =CONCAT(A1, B1, " - ", C1)
Use Case: Combines text strings.
Example:
=CONCAT(A1, " ", B1)→ Joins first and last names.
Why It’s Useful:- Merges data for labels, emails, or IDs.
11. TEXTJOIN
Formula: =TEXTJOIN(", ", TRUE, A2:A5)
Use Case: Joins text with a delimiter.
Example:
=TEXTJOIN(", ", TRUE, A2:A5)→ Combines A2:A5 with commas.
Why It’s Useful:- Creates comma-separated lists (e.g., tags, categories).
12. UNIQUE (Excel 365)
Formula: =UNIQUE(A2:A10)
Use Case: Extracts unique values from a range.
Example:
=UNIQUE(A2:A10)→ Lists distinct values in A2:A10.
Why It’s Useful:- Removes duplicates without manual filtering.
13. FILTER (Excel 365)
Formula: =FILTER(A2:B10, B2:B10="Yes")
Use Case: Filters data based on criteria.
Example:
=FILTER(A2:B10, B2:B10>100)→ Returns rows where column B > 100.
Why It’s Useful:- Dynamic data extraction for reports.
14. SORT (Excel 365)
Formula: =SORT(A2:B10, 2, TRUE)
Use Case: Sorts a range.
Example:
=SORT(A2:B10, 2, -1)→ Sorts A2:B10 by column B in descending order.
Why It’s Useful:- Automatically organizes data.
15. SORTBY (Excel 365)
Formula: =SORTBY(A2:A10, B2:B10, -1)
Use Case: Sorts a range based on another range.
Example:
=SORTBY(A2:A10, B2:B10, -1)→ Sorts A2:A10 by B2:B10 in descending order.
Why It’s Useful:- More flexible than SORT for complex sorting.
16. SEQUENCE (Excel 365)
Formula: =SEQUENCE(5, 1, 1, 2)
Use Case: Generates a sequence of numbers.
Example:
=SEQUENCE(5)→ Returns 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
Why It’s Useful:- Creates numbered lists or dynamic arrays.
17. RANDARRAY (Excel 365)
Formula: =RANDARRAY(3, 2, 1, 100, TRUE)
Use Case: Generates random numbers.
Example:
=RANDARRAY(5,1,1,100)→ 5 random numbers between 1-100.
Why It’s Useful:- Useful for simulations and testing.
25 Essential Excel Formulas
18. XLOOKUP (Excel 365)
Formula: =XLOOKUP("John", A2:A10, B2:B10, "Not Found")
Use Case: Modern alternative to VLOOKUP.
Example:
=XLOOKUP("John", A2:A10, B2:B10)→ Finds “John” and returns his data.
Why It’s Useful:- More flexible and easier than VLOOKUP.
19. XMATCH (Excel 365)
Formula: =XMATCH(100, A2:A10, 0)
Use Case: Improved MATCH function.
Example:
=XMATCH(100, A2:A10)→ Finds the position of 100.
Why It’s Useful:- Faster and more reliable than MATCH.
20. LAMBDA (Excel 365)
Formula: =LAMBDA(x, x*10)(5)
Use Case: Creates custom functions.
Example:
=LAMBDA(x, x^2)(5)→ Returns 25.
Why It’s Useful:- Enables advanced custom calculations.
21. LET (Excel 365)
Formula: =LET(x, A1*2, y, x+10, y)
Use Case: Assigns variables within a formula.
Example:
=LET(x, A1*2, x+5)→ Calculates A1*2 + 5.
Why It’s Useful:- Simplifies complex formulas.
22. ISNUMBER
Formula: =ISNUMBER(A2)
Use Case: Checks if a cell contains a number.
Example:
=ISNUMBER(A2)→ Returns TRUE if A2 is a number.
Why It’s Useful:- Validates data inputs.
23. TODAY
Formula: =TODAY()
Use Case: Returns the current date.
Example:
=TODAY()→ Displays today’s date.
Why It’s Useful:- Automates date entries in reports.
24. NETWORKDAYS
Formula: =NETWORKDAYS(A2, B2)
Use Case: Calculates working days between two dates.
Example:
=NETWORKDAYS("01-Jan-2025","31-Dec-2025")→ Counts workdays in 2025.
Why It’s Useful:- Essential for HR and project planning.
25. IFS (Excel 365)
Formula: =IFS(A1=1,"One", A1=2,"Two", TRUE,"Other")
Use Case: Multiple IF conditions in one formula.
Example:
=IFS(A1>90,"A", A1>80,"B", TRUE,"C")→ Assigns grades.
Why It’s Useful:- Simplifies nested IF statements.
25 Essential Excel Formulas
25 Essential Excel Formulas List 2025
🤔 Final Thoughts for 25 Essential Excel Formulas
These 25 Essential Excel Formulas List 2025 are your shortcut to data mastery in Excel. Whether you’re building dashboards, doing analytics, or reporting — mastering these functions will save time and improve data accuracy.
📩 If you want a free downloadable Excel practice file with all formulas, comment below or visit:
👉 excelfunclub.com/tools
🙋 FAQs for 25 Essential Excel Formulas List 2025
Are these formulas compatible with Excel 2010?
Basic formulas like SUM, IF, VLOOKUP, etc., are compatible. Modern functions like FILTER, UNIQUE, LET require Excel 365 or Excel 2021.
How can I get better at Excel formulas?
Practice with real datasets, follow tutorials on YouTube, and use tools like ExcelFunClub.
What’s the most powerful new Excel formula?
XLOOKUP and LET are game-changers for professionals working on dynamic spreadsheets.
🎯 How to Practice These 25 Essential Excel Formulas
- Try real-world scenarios like HR, sales, inventory, or student data
- Use Data Validation and Conditional Formatting alongside formulas
- Build dashboards using formulas with charts and pivot tables
🧰 Bonus Tip: Combine with Excel Shortcuts
Use keyboard shortcuts like:
Ctrl + Shift + L— Toggle filterAlt + A + M— Remove DuplicatesCtrl + E— Flash Fill
See full Excel shortcut guide here.

Hello,
I’m thrilled to write this comment for you to express my full gratitude for knowledge you’re giving to us.
I’m interesting in excel formulas but I didn’t find a proper sheet combine all needed formulas.
So please can you provide excel formula workbook (template) that contains basic and advance.
And to be considered that’s I couldn’t afford any payments right now
Thank you